Articles and Updates
April 2025
Introduction to Options on ETFs
The first exchange-traded fund (ETF) in the U.S. was the S&P 500®; Depository Receipt (SPDR®), launched by the American Stock Exchange in January 1993. Designed to track the S&P 500 Index, SPDR has been highly successful. Since its introduction, especially over the past 20 years, the growth and popularity of ETFs have increased exponentially.
What is an ETF?
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is an investment vehicle that bundles a group of securities into a single fund, similar to a mutual fund. However, unlike mutual funds, ETFs trade on an exchange throughout the day, allowing investors to buy and sell shares at market prices in real time.
What is an ETF?
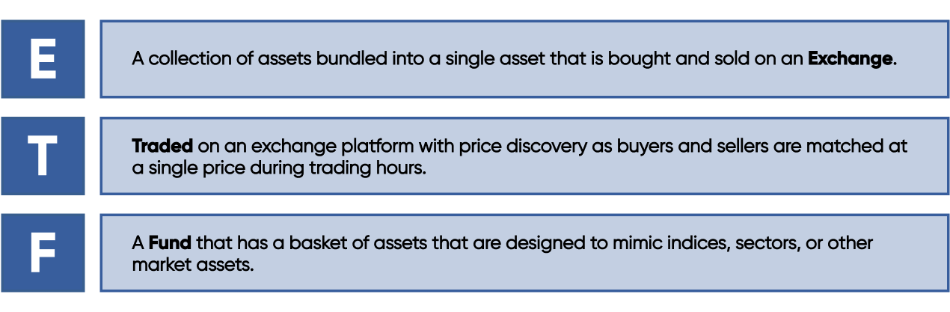
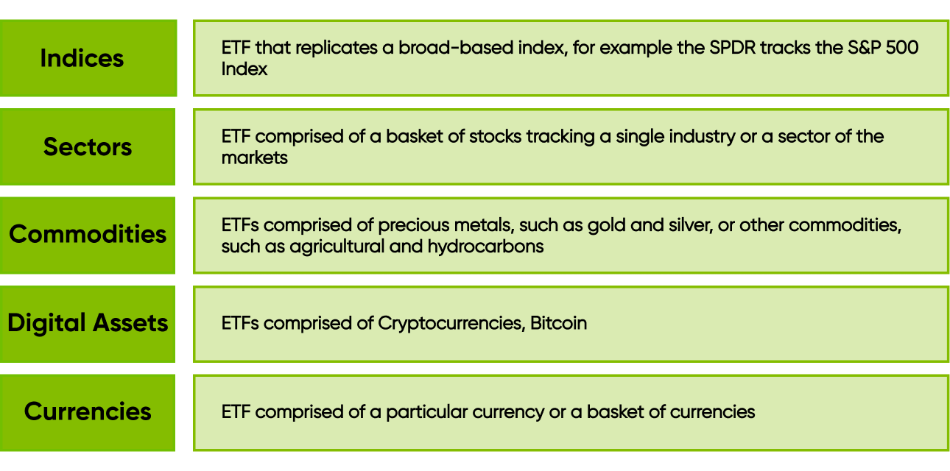
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is an investment vehicle that bundles a group of securities into a single fund, similar to a mutual fund. However, unlike mutual funds, ETFs trade on an exchange throughout the day, allowing investors to buy and sell shares at market prices in real time.Types of ETFs

Motivations for Trading ETF Options
- Broad Market Exposure - ETFs can provide access to a range of assets within a single trade.
- Diversification - Investing in an ETF helps reduce single-stock risk from earnings and news events.
- Sector-Based Trading - Investors can trade an entire sector without having to buy individual stocks.
Trading Options on ETFs
Options on ETFs function similarly to equity options, providing risk management and portfolio hedging opportunities. By combining ETFs with options, investors can implement various strategies to align with their market outlook. ETF options also benefit from transparent trading on regulated exchanges and are cleared by the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC), ensuring fulfillment guarantees.ETF Options: Strategy Examples
- Covered Call - Involves holding a long ETF underlying position while selling a call option. The investor collects the option premium in exchange for limiting potential upside gains if the ETF price rises beyond the strike price of the call.
- Protective Put - A risk management strategy where an investor holds a long ETF underlying position and buys a put option to hedge against potential declines while maintaining upside exposure.
- Collar - A defensive strategy combining a long ETF underlying position, a protective put, and a covered call to limit downside risk in exchange for limited upside potential while financing the cost of the hedge with the premium received when selling the call.

